Change Hard Drive Serial Number Linux

An overview of how HDDs work A hard disk drive ( HDD), hard disk, hard drive or fixed disk is a that uses to store and retrieve information using one or more rigid rapidly rotating disks () coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with, usually arranged on a moving arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces.
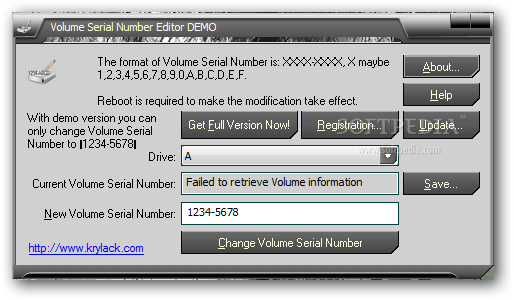
House Party Lop Game Download here. A volume serial number is a number given to a drive during the format process. Here's more on volume serial numbers, how they're generated, and more.
Data is accessed in a manner, meaning that individual of data can be stored or retrieved in any order and not only. HDDs are a type of, retaining stored data even when powered off. Introduced by in 1956, HDDs became the dominant device for by the early 1960s. Hindu Wedding Invitation Cards Psd File. Continuously improved, HDDs have maintained this position into the modern era of and. More than 200 companies have produced HDDs historically, though after extensive industry consolidation most current units are manufactured by,, and. HDD unit shipments and sales revenues are declining, though production (exabytes per year) is growing. Has a growing share of the market for secondary storage, in the form of (SSDs).
SSDs have higher data-transfer rates, higher areal storage density, better reliability, and much lower latency and access times. Though SSDs have higher cost per bit, they are replacing HDDs where speed, power consumption, small size, and durability are important. The primary characteristics of an HDD are its capacity and. Capacity is specified in corresponding to powers of 1000: a 1- (TB) drive has a capacity of 1,000 (GB; where 1 gigabyte = 1 billion ). Typically, some of an HDD's capacity is unavailable to the user because it is used by the and the computer, and possibly inbuilt redundancy for and recovery. Performance is specified by the time required to move the heads to a track or cylinder (average access time) plus the time it takes for the desired sector to move under the head (average, which is a function of the physical in ), and finally the speed at which the data is transmitted (data rate).
The two most common for modern HDDs are 3.5-, for desktop computers, and 2.5-inch, primarily for laptops. HDDs are connected to systems by standard cables such as (Parallel ATA), (Serial ATA), or SAS () cables. Main article: Improvement of HDD characteristics over time Parameter Started with (1956) Developed to (2017) Improvement Capacity (formatted) 3.75 megabytes 14 terabytes 3.73-million-to-one Physical volume 68 (1.9 ) 2.1 (34 ) 56,000-to-one Weight 2,000 (910 ) 2.2 (62 ) 15,000-to-one Average access time approx. 600 milliseconds 2.5 ms to 10 ms; RW RAM dependent about 200-to-one Price US$9,200 per megabyte (1961) US$0.032 per gigabyte by 2015 300-million-to-one Data density 2,000 per 1.3 terabits per square inch in 2015 650-million-to-one Average lifespan ~2000 hrs MTBF [ ] ~2500000 hrs MTBF 1250-to-one The hard disk drives was initially developed as data storage for an IBM real-time which became the., IBM announced HDDs in 1956 as a component of the IBM 305 RAMAC system and as new component to enhance the existing system, a general-purpose. The first IBM drive, the in 1956, was approximately the size of two medium-sized refrigerators and stored five million six-bit characters (3.75 ) on a stack of 50 disks. In 1962 the IBM 350 RAMAC disk storage unit was superseded by the IBM 1301 disk storage unit, which consisted of 50 platters, each about 1/8-inch thick and 24 inches in diameter. Whereas the IBM 350 used only two read/write heads which were pneumatically actuated and moved in two dimensions, the 1301 was one of the first disk storage units to use an array of heads, one per platter, moving as a single unit.